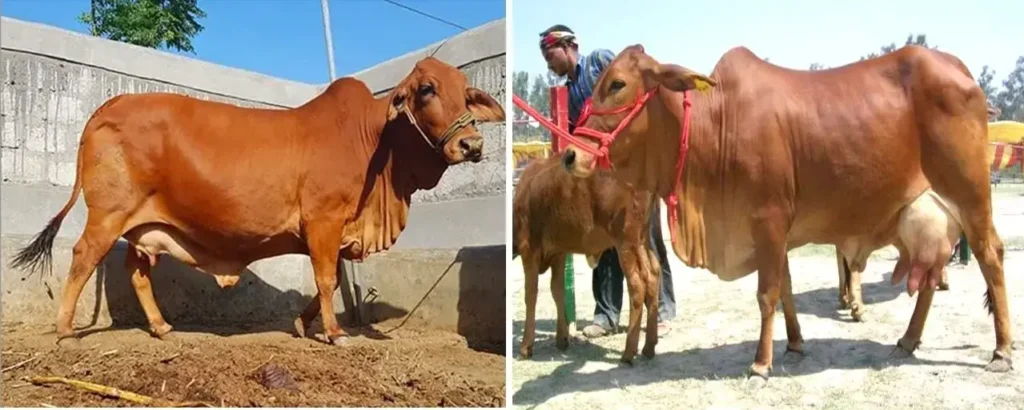
The Sahiwal cattle are considered the best breed indigenous to the Indian subcontinent. Sahiwal is one of the breeds with a high milk yield of 3000-4000 kg per year with high butterfat content. It is among the few breeds in India that can compete with exotic breeds which offer very high milk yield and make dairy farming profitable. But being an Indian breed the Sahiwal has its benefits. This article is dedicated to the Sahiwal Cattle which stands tall among Indian cattle breeds.
Sahiwal Cow characteristics
Sahiwal cows, revered for their exceptional qualities, are a prominent breed of Zebu cattle originating from the Punjab region of Pakistan and India. Let’s delve into the key physical characteristics that define these remarkable bovines.
Physical Appearance of Sahiwal
- Sahiwal cows are a breed of Zebu cattle primarily found in the Punjab region of Pakistan and India.
- They have reddish-brown colored coats.
- Sahiwal cows have a compact and sturdy build with a moderate to large frame size.
- Adult cows typically weigh between 400 to 600 kilograms (880 to 1320 pounds), with some exceptional individuals reaching up to 700 kilograms (1540 pounds).
- Height at withers, which is the highest point on the back of the animal, ranges from 130 to 140 centimeters (51 to 55 inches).
- Their horns are short to medium in length, curved slightly outward, and can reach up to 50 centimeters (20 inches) in length.
- Sahiwal cows have well-developed udders with average milk production ranging from 2,000 to 3,000 kilograms (4400 to 6600 pounds) per lactation cycle.
- Milk from Sahiwal cows has a high butterfat content, typically around 4.5% to 5.5%, making it desirable for dairy production.
Fertility of Sahiwal breed
The Sahiwal cows exhibit remarkable reproductive capabilities, characterized by high conception rates, regular estrus cycles, and efficient calving intervals. One of the notable aspects of Sahiwal cow fertility is their early sexual maturity. Female Sahiwal calves typically reach puberty at an early age, often between 12 to 15 months, compared to other cattle breeds. Their regular estrus cycles, typically lasting around 21 days, enable breeders to plan and optimize breeding schedules effectively.
Milk Production and Lactation of Sahiwal Cow
Sahiwal cows are renowned for their exceptional milk production capabilities, making them a prized breed in the dairy industry.
On average, Sahiwal cows produce between 2,000 to 3,000 kilograms (4400 to 6600 pounds) of milk per lactation cycle, although some exceptional individuals may produce even more. This milk production level is impressive considering the moderate to large frame size of Sahiwal cows.
Sahiwal cows typically have well-developed and capacious udders, allowing for efficient milk storage and secretion. Their teats are well-positioned and easy to milk, facilitating the milking process and reducing labor requirements.
Furthermore, Sahiwal cows exhibit a relatively long lactation period compared to some other cattle breeds. The average lactation period for Sahiwal cows ranges from 250 to 300 days, although individual variations may occur.
The milk produced by Sahiwal cows is characterized by its rich flavor and creamy texture, attributed to its high butterfat content. Typically, Sahiwal cow milk contains around 4.5% to 5.5% butterfat, although variations may occur depending on factors such as diet and management practices.
Calves Features of Sahiwal breed
- At birth, Sahiwal calves typically weigh between 20 to 25 kilograms (44 to 55 pounds), showcasing their robustness and vigor from an early age.
- Sahiwal calves exhibit excellent feed conversion efficiency, with feed conversion ratios comparable to or better than other cattle breeds.
- These calves have a calm and docile temperament
- With proper nutrition and management, Sahiwal calves can achieve rapid weight gain, reaching weaning weights of 100 to 150 kilograms (220 to 330 pounds) by 6 to 8 months of age.
Cost of Sahiwal Cow
The cost of Sahiwal Cows varies depending on the milk production, age, and physical condition. However, being the finest cattle breed in India, the Sahiwal cow can fetch Rs.60,000-75,000 in the Indian market.

Also Read
Management of Sahiwal Cows
Effective management practices are paramount for the success and sustainability of Sahiwal cow operations. Let us look at various management practices which are crucial for the development of Sahiwal cows.
Housing Requirements of Sahiwal Cows
Proper housing and shelter are crucial for the proper growth and productivity of Sahiwal cows. Here are the aspects you have to consider about housing Sahiwal cows.
- The shelters should protect against rain, wind, and extreme temperatures. Adequate insulation and drainage are necessary features.
- Comfortable bedding, such as straw or sawdust, should be provided for cleanliness and moisture absorption. Regular replacement of bedding maintains hygiene.
- Feeding areas should offer easy access to clean feed and sufficient trough space to prevent competition.
- Secure fencing around the housing area prevents wandering and protects against predators. The recommended space per cow is 80-100 square feet, considering age, size, and lactation status.
- Optimized natural lighting promotes natural rhythms and well-being, while supplemental lighting may be necessary in darker seasons or regions.
- Regular cleaning, disinfection, deworming, and vaccination schedules maintain a hygienic environment and prevent disease spread.
- For instance, housing 50 Sahiwal cows requires approximately 4000-5000 square feet. Each cow consumes around 20-30 gallons of water daily.
Feed Requirements of Sahiwal Cows
Here’s an overview of the feed requirements for Sahiwal cows:
1. Forage and Roughage:
- Sahiwal cows primarily thrive on a diet rich in forage and roughage. Good-quality green fodder, such as alfalfa, clover, and maize, should form the basis of their diet.
- The recommended daily intake of forage and roughage for Sahiwal cows is around 2-2.5% of their body weight.
2. Concentrates:
- In addition to forage, Sahiwal cows require concentrates to meet their energy and protein needs, especially during periods of lactation and gestation.
- As a general guideline, concentrates should constitute around 0.5-1% of the cow’s body weight per day.
3. Minerals and Vitamins:
- Sahiwal cows need access to mineral supplements to ensure proper growth, reproduction, and overall health.
- Providing mineral supplements in the form of mineral blocks or loose minerals ensures that Sahiwal cows receive all the necessary nutrients.
4. Water:
- Access to clean and fresh water is essential for Sahiwal cows’ health and milk production.
- On average, a Sahiwal cow consumes around 20-30 gallons of water per day, depending on factors such as ambient temperature, lactation stage, and feed moisture content.
5. Feeding Management:
- Feed should be provided in multiple small meals throughout the day to promote efficient digestion and nutrient absorption.
- Regular monitoring of body condition score and feed intake helps adjust the diet according to individual cow requirements.
Disease and Pest Management and Vaccination
Effective disease and pest management, along with vaccination protocols, are crucial for maintaining the health and productivity of Sahiwal cows. Here’s a detailed overview:
1. Disease Management:
- Sahiwal cows are susceptible to various diseases, including mastitis, foot rot, respiratory infections, and parasitic infestations.
- Regular monitoring of cows for signs of illness, such as changes in behavior, appetite, or milk production, is essential for early detection and treatment.
- Implementing biosecurity measures, such as quarantine protocols for new animals and restricting visitor access, helps prevent the introduction and spread of infectious diseases.
2. Pest Management:
- External parasites, such as ticks, mites, and flies, can irritate, and discomfort, and transmit diseases to Sahiwal cows.
- Providing adequate shelter, maintaining proper hygiene, and implementing fly control measures, such as fly traps or insecticide application, help reduce pest infestations.
3. Vaccination:
- Common vaccines for Sahiwal cows include those for diseases such as bovine viral diarrhea (BVD), infectious bovine rhinotracheitis (IBR), bovine respiratory syncytial virus (BRSV), leptospirosis, and clostridial infections.
- Vaccination schedules should be developed in consultation with a veterinarian based on factors such as the cow’s age, health status, and local disease prevalence.

Advantages and Disadvantages of Sahiwal Cows
Advantages of Sahiwal Cows
The advantages of Sahiwal cows are
1. High Milk Yield: Sahiwal cows are renowned for their exceptional milk production, often surpassing other indigenous breeds.
2. Heat Tolerance: Originating from the hot and humid climate of the Sahiwal region in Punjab, Pakistan, these cows exhibit excellent heat tolerance.
3. Adaptability: Sahiwal cows are highly adaptable to various environmental conditions. Whether it’s changes in temperature, humidity, or forage availability, they can adjust and continue to perform well.
4. Resilience: This breed is known for its hardiness and resilience against diseases and pests.
5. Efficient Feed Conversion: Sahiwal cows are efficient converters of feed into milk, requiring less feed input compared to other breeds to maintain their high milk yields.
Disadvantages
1. Slow Growth Rate: While Sahiwal cows excel in milk production, they have a relatively slower growth rate compared to some other breeds. This may not make them ideal for beef production purposes where rapid weight gain is desired.
2. Limited Market Demand: In regions where Sahiwal cows are not well-known or recognized, there may be limited market demand for their milk or breeding stock. This can affect the profitability of dairy farming enterprises relying solely on Sahiwal cows.
3. Longevity: Sahiwal cows tend to have a longer calving interval compared to some other dairy breeds. This may result in lower overall productivity over their lifespan, especially if not managed effectively through proper breeding and reproductive management practices.
4. Space Requirements: Like many other cattle breeds, Sahiwal cows require adequate space for grazing and housing. In densely populated areas or regions with limited land availability, providing sufficient space for a Sahiwal herd may pose a challenge.
Crossbreeding Programs Involving the Sahiwal Cow
Here’s an overview of crossbreeding programs involving Sahiwal cows:
1. Objective:
- The primary goal of crossbreeding programs is to develop hybrids with enhanced traits that meet specific production or environmental challenges.
- Common objectives include improving milk yield, growth rates, reproductive performance, and adaptability to different climates and management systems.
2. Selection of Parent Breeds:
- Sahiwal cows are often crossed with exotic dairy breeds known for their high milk production, such as Holstein Friesian , Jersey.
- Exotic breeds contribute genes for increased milk yield, while Sahiwal genetics provide heat tolerance, disease resistance, and adaptability to local conditions.
3. Breeding Strategies:
- Various breeding strategies can be employed, including rotational crossbreeding, terminal crossbreeding, and backcrossing, depending on the specific objectives of the program.
- Rotational crossbreeding involves alternating between Sahiwal and exotic breeds over successive generations to maintain hybrid vigor and maximize the complementary traits of both breeds.
- Terminal crossbreeding involves crossing Sahiwal cows with exotic sires to produce calves for specific purposes, such as beef production or replacement heifers for further breeding.
- Backcrossing involves crossing hybrid offspring back to one of the parental breeds to reinforce desired traits while retaining some level of hybrid vigor.
4. Evaluation and Selection:
- Rigorous selection criteria are applied to identify animals with desirable traits for inclusion in the breeding program.
- Traits such as milk yield, reproductive efficiency, growth rate, conformation, and health are evaluated to ensure progress toward program objectives.
- Genetic evaluations, performance testing, and pedigree analysis are commonly used tools to assess the breeding value of individual animals and inform selection decisions.
5. Implementation Challenges:
- Crossbreeding programs require careful planning, management, and monitoring to achieve desired outcomes while minimizing undesirable genetic effects.
- Challenges may include maintaining breed purity, managing genetic diversity, and addressing potential negative effects on certain traits, such as fertility or longevity.
- Adoption of crossbreeding strategies may also face resistance or skepticism from traditionalists or stakeholders unfamiliar with the benefits of hybrid vigor and genetic improvement.
6. Long-Term Impact:
- Crossbreeding programs involving Sahiwal cows have the potential to significantly improve the productivity, resilience, and profitability of dairy farming operations in various regions.
Also Read
- Top 10 Buffalo Breeds in India
- HF Cow (Holstein Friesian): Characteristics, Cost, HF Cow Milk Per Day and Management
- Top 20 Goat Breeds in India
Summing Up
Sahiwal cows are the best breed of cows native to India. For years they have been competing with exotic and crossbred cattle breeds, but have still maintained their position in Indian markets as one of the most popular cows in Indian farmers. They are the highest milk producers among indigenous breeds and possess a high butterfat content that is favorable among farmers. But to ensure that they produce high quantities of milk, proper housing, and hygiene should be maintained. Along with that, they have to be fed nutritious fodder and supplements. Vaccinations and disease management practices have to be done to ensure the good health of the cattle and high productivity.
Latest Post
- Study Agriculture Abroad : A Complete Guide for USA
- July Issue (2024): Times of Agriculture Magazine
- Why Money Plant is called Money Plant ? Answer in 5 min
- How to grow Monstera from Cutting: 5-Step Detailed Guide
- Latest 10 Finest Terrace Garden Ideas to Transform Your Rooftops
- Top 10 Low Light Hanging Plants to make your Room Crunchy
- Best Water Harvesting Techniques for a Sustainable Future
- Low Maintenance Indoor Plants for India: 15 Best plants for home gardening
- Top 23 Flowering Trees in India: Flower Tree for Home