Hello, my super excited growers! Have you ever thought about the aromatic bark you enjoy almost every day in a sweet and savory dish?? If you are curious to know more about cinnamon or dalchini, please pay your valuable attention to it. I assure you that you will enjoy the article about cinnamon and how to grow cinnamon is an appropriate way to enjoy it and earn profit by growing it.
Cinnamon (Cinnamomum verum) is an evergreen spice plant that belongs to the family Lauraceae ( native- Sri Lanka). Cinnamon is used to enhancing the flavor of food due to its aroma, and that aroma comes from the essential oils present in it like cinnamaldehyde, eugenol, etc.
Types of Cinnamon in india
| No. | Variety/Types | Scientific name | Characters |
| 1. | Indonesian cinnamon or Padang cinnamon or Korintje cinnamon | Cinnamomum burmanni | It has a mild taste and fits in every dish. Very common in America. |
| 2. | Chinese cinnamon | Cinnamomum cassia | It is sweet but not super spicy. Found in supermarkets. |
| 3. | Vietnamese cinnamon or Saigon cinnamon | Cinnamomum loureiroi | Called Royal cinnamon, sweet and spicy cinnamon, cultivated in Vietnam. Fits in the grocery store for sale as it is very hard. |
| 4. | Malabar cinnamon | Cinnamomum citriodorum | It has a unique smell of lemon grass. |
Nutritional Values of Cinnamon:
| Components | Quantity (per 100 g) |
| Carbohydrate | 80 g |
| Water | 11 g |
| Protein | 4 g |
| Fat | 1.2 g |
| Energy | 1,035 KJ |
| Vitamins | |
| Vitamin A | 15 µg |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.02 mg |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.04 mg |
| Vitamin B3 | 1.33 mg |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.16 mg |
| Vitamin B9 | 6 µg |
| Vitamin C | 3.8 mg |
| Vitamin E | 2.3 mg |
| Vitamin K | 31.2 µg |
| Minerals | |
| Calcium | 1002 mg |
| Potassium | 431 mg |
| Phosphorus | 64 mg |
| Magnesium | 60 mg |
| Sodium | 10 mg |
| Iron | 8.3 mg |
| Zinc | 1.8 mg |
Grading of Cinnamon
According to the Sri Lankan grading system, it is divided into 4 groups-
| Type | Parameter |
| Alba | < 6 mm in diameter |
| Continental | < 16 mm in diameter |
| Mexican | < 19 mm in diameter |
| Hamburg | < 32 mm in diameter |
- Quills: a piece of cinnamon bark < 106 mm long is called a quill. On the basis of quill diameter and number of quills per kg, Mexican is divided into further three categories – M00000 special, M000000, and M0000.
- Featherings: it is the inner bark of twigs and twisted shoots.
- Chips: Chips are the bark of small twigs that can’t be separated.
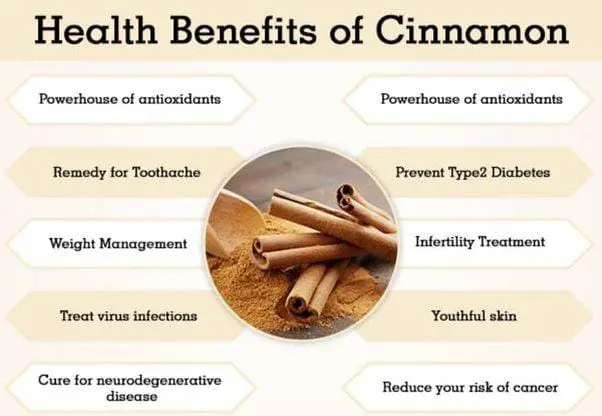
Health Benefits of Cinnamon
Although cinnamon is considered as a spice but it has a huge health due to contain various types of antioxidants, essential oils, and other beneficial components.
- Cinnamaldehyde present in cinnamon has a huge medicinal value. It increases metabolic activity, maintains glucose levels in the body, etc.
- Cinnamon has a large quantity of polyphenol antioxidants.
- It is reported that cinnamon has anti-inflammatory properties.
- Everyday consumption of 1.5 gm of cinnamon can reduce the chance of heart disease by reducing levels of triglycerides, cholesterol, and blood sugar.
- Insulin sensitivity is increased by the consumption of cinnamon
- Consuming cinnamon 1 to 6 g per day is very beneficial for maintaining blood sugar levels.
- It is reported that Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s diseases like neurodegenerative diseases are prevented by cinnamon as it maintains the activity of neurotransmitters.
- Anti-viral and anti-fungal properties are possessed by cinnamon as it contains Cinnamaldehyde.
Some Important Facts:
Two high-yielding, profitable varieties released by IISR, namely- Naveshree and Nithyashree, are very suitable in Indian climatic conditions for cultivation. Let’s see the difference between the two varieties.
| Variety | Features |
| Naveshree | Yield – 56 kg quills/ha, Bark oil-2.7%, Leaf oil- 2.8%, Cinnamaldehyde-73%, Bark oleoresin- 8% |
| Nithyashree | Yield – 54 kg quills/ha, Bark oil-2.7%, Leaf oil- 3%, Cinnamaldehyde-58%, Bark oleoresin- 10%, Eugenol – 78% |
How to Grow Cinnamon Plants
Propagation Methods of Cinnamon:
1- Cutting:
semi-hardwood is cut at a length of 10cm with 2 leaves, and dipped in rooting hormones like Rootex, Karedix-B, etc. Then plant it in a mixture of sand and coir dust in a 1:1 ratio. Place the pot in shade and watered regularly 3 times a day.
2- Air Layering:
This is done by removing a portion of semi-hardwood from the bark and applying rooting hormone (like Rootex, Karedix-B). Then cover this part with coir husk and wrap it with a polythene sheet. After 40 to 60 days rooting will take place.
Preparation of Land
At first, you have to dig a pit sized 50cm*50cm*50 cm and make the pits at a spacing of 3m*3m. Then organic compost and topsoil are filled into the pit. Organic compost helps to increase beneficial soil microorganisms that will boost the growth of the cinnamon plant.
Planting of Cinnamon Plant:
June- July is the most suitable month for planting cinnamon plants so that plants will get plenty of water in the monsoon.
How to Grow Cinnamon by Transplanting:
The seedlings that are 10 to 12 months old or cuttings (well-rooted), and disease-free are used as transplanting materials. 3 to 4 seedlings are transplanted in each pit.
How to Grow Cinnamon by seed:
The dibbling method of seeding is very helpful for cinnamon planting. After putting the seed it should be covered with compost and soil.
Selection of Seeds:
Seed is one of the most important components of a plant. that’s why the selection process of seed is also very crucial. Collect seeds from a trusted organization or from a renowned source.
Fertilizer Application:
For the growth and development of plants, Fertilizer is a very important component. In the first year nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium should be applied at a dose of 20g, 18g, and 25 g respectively. The fertilizer dose of Nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium will increase gradually up to 200g, 180g, and 200 g respectively according to plant age. Fertilizer should be applied in 2 equal split doses for better results (in May-June and September-October). Mulching green manuring, FYM should be recommended at a dose of 25 kg.
Climatic Requirement for the Cinnamon Plant
Plants get the maximum of the nutrients from the soil.so, soil plays a very significant role in the proper growth of cinnamon plants. Cinnamon plants grow best in laterite soil and also in sandy soil. It requires 200 cm to 250 cm of annual rainfall as it is a rainfed crop.
Light Requirement of Cinnamon Plant:
Light plays a very crucial role in the growth and development of the cinnamon plant. Almost six to eight hrs of direct sunshine is needed for proper growth. Cinnamon plants prefer hot and dry climates and in the seedling stage, shade is important.
Water Requirement:
Cinnamon is the monsoon-loving plant, so soil moisture plays a crucial role. During scarcity of rain irrigation should be provided properly.
Temperature Requirement:
A warm climate of about 80 degrees F enhances the growth of the plant. The growth will resist at below 40 degrees F.
pH Requirement:
cinnamon plant prefers an acidic to neutral pH range of 6.2 to 7.2.
Also Read
Insect Pest and Disease Management of Cinnamon Plant:
The cinnamon plant is infested by a lot of pests as well as diseases. Some important insect pests are described below-
| Name of insect | Damage symptoms | Management |
| Cinnamon butterfly(Chilasa clytia) | Defoliation of leaf. In severe infestation, only midribs and veins are left. | The application of quinalphos 0.05% is effective. |
| Leaf miner(conopomorpha civica) | Create mines by feeding between two epidermis. Leaves become crinkled and blister-like patches form. | The application of quinalphos 0.05% during the emergence of new flushes is effective. |
| Mealybugs | Suck the sap from the leaf and make the plant weak, yellowing of leaves. | Any systemic insecticide is effective. |
Important Diseases of Cinnamon-
| Name of disease | Symptoms | Management |
| Seedling blight(Diplodia sp.) | Light brown patches girdle the stem. Plants become weak resulting in mortality. | Spray 1% Bordeaux mixture. |
| Leaf spot(Colletotrichum gloeosporioides) | Deep brown spots on the leaves, irregular patches with shot holes. | Pruning of branches and application of Bordeaux mixture is effective. |
| Grey blight(Pestalotia palmarum) | Grey spot with a brown border. | 1% Bordeaux mixture. |
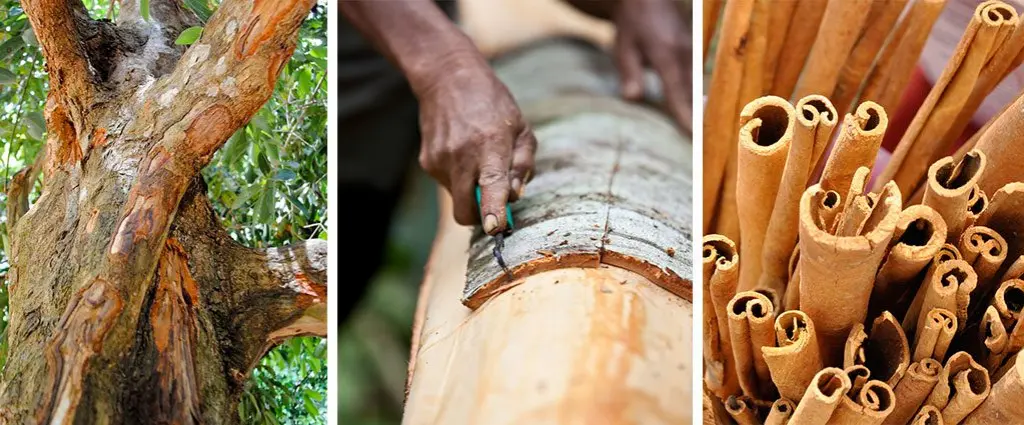
Harvesting Process of Cinnamon Bark and Oil
At the age of 2 years of planting (almost 12cm hight), the first cutback is followed to encourage the growth of the side shoot.
Commercial harvesting is done from 4th year onward. The ideal condition for harvesting cinnamon shoots is at 1.5 to 2 cm thickness and uniform brown color. Test cut is performed to check the suitability of harvesting. Then coppicing is done if the bark separates easily from shoots during test cut.
You have to cut the shoot at 1 to 1.25 m length then peeling and separation is performed. A special type of knife is used in peeling which has a small round end with a sided projection.
The peeled bark is kept overnight under shade. Then dry it in sunlight for 4 days to give it a proper quill appearance. After that, they are sent for grading. Various parameters are there for grading.
Cinnamon oil is extracted by the distillation process. Dried leaves and bark are used to extract oil. you will get 4kg of bark oil from a one-hectare plantation which is widely used in perfume, soap, and cosmetic industries.

Also Read
Conclusion:
Growing cinnamon, a pleasant, satisfying aromatic spice can give the growers another level of joy. It is a blessing that we came to know from our ancestors about this aromatic spices are used not only as spices in culinary sectors but also have great value in the medicinal sector. This article provides you with chrystal clear knowledge about how to grow cinnamon plants. With proper care, maintaining all the abiotic factors, and seed quality you can easily enjoy the taste of flavors and can earn a good profit.
Latest Post
- February 2026 – Times of Agriculture Magazine
- January Issue 2026- Times of Agriculture Magazine
- Top 10 Agricultural Drone Companies in India
- December Issue 2025- Times of Agriculture Magazine
- November Issue 2025- Times of Agriculture Magazine
- Punjab & Sind Bank Introduces Special Program to Support Food and Agro-Processing Sector
- Beyond Classrooms and Gardens: How a Professor Turned His Passion into Purpose
- October Issue 2025- Times of Agriculture Magazine
- Top 10 Pesticide Companies in the World











