Organic farming is the new vogue in the Indian agriculture sector. With a pressing global focus on sustainable development, climate change, and carbon emissions along with conventional farming becoming repugnant due to the overuse of diabolical chemicals, there is no choice other than to revert to organic farming practices. The concomitant surge in organic farming practices will be met with questions about the credibility of its products. That is why organic certification is essential.
Organic certification serves as a piece of unparalleled evidence for the credibility of organic products. Organic certification is an imperative label for farmers or organizations practicing organic farming. Indian organic certified products are accepted in India, North America, and the European Union. In addition to serving as an assurance of credibility, the certification helps fetch a premium price for the produce.
Organic Certification
Organic certification refers to the compilation of all processes in granting the Indian Organic Certification to the eligible farmer.
It is a rigorous process involving intense scrutiny of the applicant’s details to check whether he/she is eligible for the certification. The scrutiny is based on certain standards or requirements that need to be satisfied for certification.
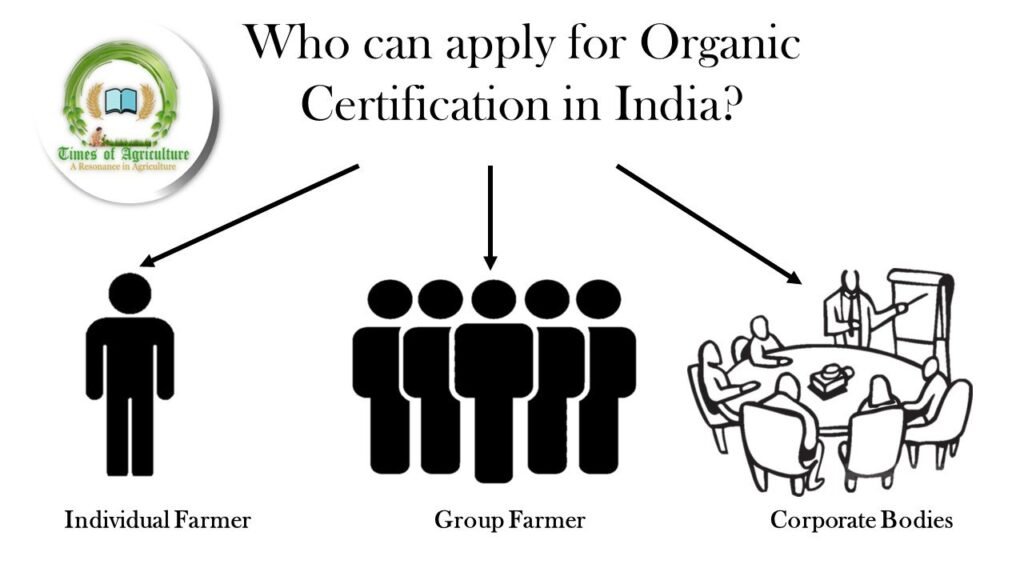
Who can apply for Organic Certification?
Registration for organic certification can be done by
- Individual Farmers: a farmer who is the legal owner of a particular piece of land, however large it may be, can apply for the organic certification label.
- Groups of Farmers: a conglomerate of two or more farmers of the same revenue district can apply. There is no restriction on the area of land. However, the number of farmers owning 10 acres of land should be less than 50% of the total group.
- Corporate bodies: it mainly refers to the association of farmers who come together to register as a corporate body. They can produce, process, and sell organic produce but they should have an office setup to monitor the activities of the farm.
Read More:
how to get organic certification in india
The process of organic certification involves several steps and a perspicuous understanding of each step is a must for the farmers to gain certification. The main steps are

Step 1: Understanding the Organic Certification Requirements
Understanding the requirements for the certification process is a prerequisite for organic certification. In India, these standards or requirements are set forth mainly by two agencies
- NPOP: National Programme for Organic Production
- PGS-India: Participatory Guarantee System of India
These agencies construct the standards that each applicant for organic certification must abide by to be conferred with the certification.
The NPOP is a central government body that regulates the certification process and other aspects of organic farming. In contrast, the PGS is a guarantee system that ensures the participation of stakeholders in the certification process.
The NPOP has established numerous requirements that need to be complied with by the farmers to be certified. The main requirements are
- Conversion: The land that was used for conventional agricultural practices must undergo a conversion to organic practices. This includes the prohibition of synthetic chemicals and Genetically Modified Organisms (GMOs). This conversion usually takes about 2 to 3 years.
- Land: The land should be free from any kind of restricted substances and should maintain buffer zones to prevent contamination from non-organic sources.
- Agricultural inputs: Organic seeds, organic fertilizers, and organic plant protection substances should be used on the farm. The use of GMOs or any chemical fertilizer or pesticide will compromise the certification.
- Farm records: Records should be kept to document all the activities occurring on the farm like seeds used, fertilizers used, irrigation time, etc.
- Management plan: Farmers should maintain a management plan outlining all the activities that are to be done on the organic farm. It serves as the blueprint of all activities on the farm.
- Labeling: After successful completion of the certification process, the certified farmers can use the Indian Organic logo on their products. However, the use of this logo in labeling and packaging should comply with the NPOP standards of packaging and labeling.
- Post-Certification: the certified organic producers must continue to abide by the rules and regulations of NPOP to maintain their certification. They must undergo periodic inspections of their land to update their status. In case of any misconduct, the certification will be suspended or revoked.
Organic farming in India is a dynamic venture. The NPOP may revise its standards in the coming years. Therefore individuals seeking certifications should always update themselves on the latest NPOP guidelines and tweak their management plans accordingly.
Step 2: organic certification agencies in india
The NPOP is the main regulatory body concerned with organic certification. However, NPOP has dispersed this power with certain agencies throughout India. These agencies are responsible for inspecting the farms to check whether the NPOP standards are met for conferring the certification.
So once the NPOP and PGS-India requirements for organic certification are understood, the next important step is to select a certifying agency that is accredited by the Agricultural and Processed Food Products Export Development Authority (APEDA).
Plenty of accredited bodies under the NPOP conduct surveys and inspections for organic certification. Few of them are
A person looking for organic certification has to contact any one of the nearest accredited certification agencies which will guide you through the process. The cost for further proceedings varies with the agency selected.
The applicant should probe into the track record, history of certifications done, the costs charged, and the overall reputation of the agency before providing the application for certification.

After a proper understanding of the requirements for organic certification, and selecting a suitable agency after adequate research, the next step is application and documentation, a crucial step in the process.
Read More:
Step 3: Application and Documentation
After the selection of the certifying agency, the next step is submitting the application form containing the complete details of the applicant, and his farm.
The application form for registration should contain information on the name and address of the applicant, the venture for which the certification is intended, the total area of land, total land holdings, and other details.
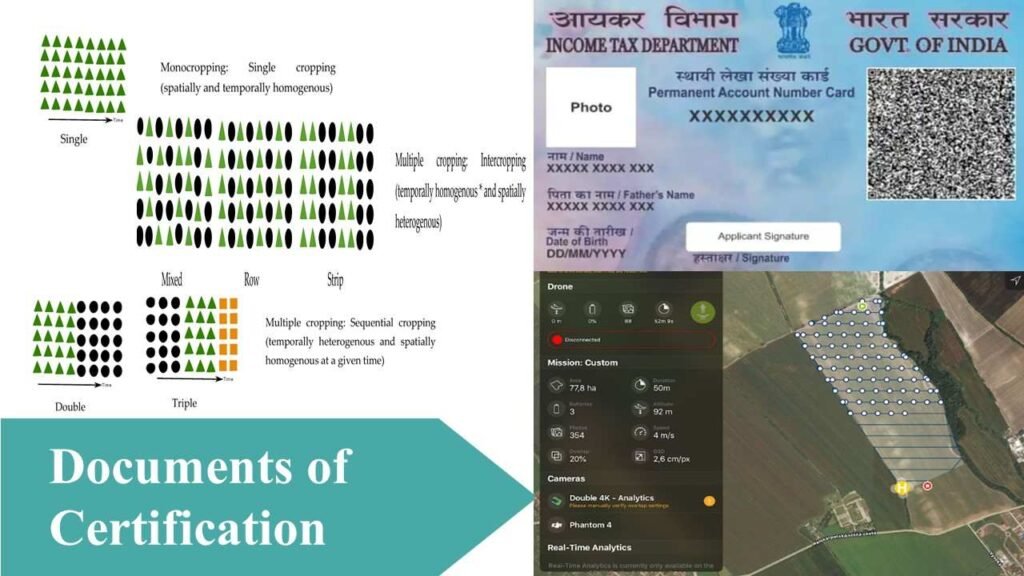
The applicant should also produce additional documents like
- Duplicate of the application form
- PAN card
- Annual cropping pattern
- Field map
- General details of the farm
- Soil and water analysis report
- Land document details
- Written annual production plan
The annual production plan should be a wholesome document containing information on seeds used, the activities done for nutrient management and plant protection, methods of harvesting, and storage activities.
Along with these documents, the applicant is required to remit a certain fee associated with his application. The fee to be remitted for organic certification varies with the agency selected by the applicant and also according to the applicant.
The fee structure for application for organic certification as per the Tamil Nadu Organic Certification Department is as follows
Fee structure per farm unit of a farmer
| Sl. No. | Item | Certification only on NPOP(in Rupees) | Certification on Foreign Standards(in Rupees) | Remarks |
| 1 | Registration Fee | ₹500/- for small and marginal farmers₹1000/- for other farmers | ₹1000/- | Annual renewal fee 25% of the registration fee |
| 2 | Fee for inspection and certification | ₹1000/- per day | ₹1200/- per day | For preparation inspection and certification work |
| 3 | Fee for travel time | ₹200/- per day | ₹200/- per day | NIL |
| 4 | Travel expenses | Actual | Actual | For travel, food and accommodation when applicable |
| 5 | Fee for scope certificate | ₹1000/- | ₹1500/- | The added value of widely recognized certificate |
| 6 | Fee for transaction certificate if required | ₹500/- | ₹1000/- | |
| 7 | Chemical analysis if required | Actual cost | Actual cost | Soil samples, water, leaf samples, and product sample. |
The above fee structure is for a single farmer. The fee structure is different for groups of farmers and corporate or business categories.
The application and documentation process is necessary for the certifying agency to assess the compliance of farm activities as per the NPOP standards. This is crucial to obtain organic certification.
Step 4: Inspection
Upon receiving the application and documentation, the selected certifying agency conducts an on-site inspection of the farm. Qualified professionals of the agency will conduct an elaborate tour of the applicant’s fields. Along with on-site inspection, the examination of records as well as an interview of the applicant is done.
The daily activity record is an important document that will be thoroughly checked. The activities of the farm will be inspected to verify the information in the records and ensure that these activities comply with the NPOP guidelines.
Further, the inspector has the right to collect soil samples and send them for laboratory analysis to check the presence of any restricted chemical application in the field.
The farmers must be available for inspection at any time. In addition to this, surprise inspections will also be done by the certification officer. The inspection is a crucial step in the certification process and can be done multiple times as per the officer’s convenience.
Step 5: Compliance and Correction
Based on the field inspections done, the certifying agency will notify the shortcomings of the field to the farmer. A detailed list of areas that need to be modified to adhere to NPOP norms will be provided. It is the sole responsibility of the farmer or the business to make the required corrections as soon as possible to meet the requirements of the certification agency.
Step 6: Certification Decision
After the inspection procedure, the certification agency reviews the findings. If the certification agency finds that the applicant has complied with all the NPOP norms in his practices, the certification agency confers the organic certification to the farmer.
The validity of the organic certificate is 3 years and after that, it needs to be renewed.
On receiving the organic certificate, the farmer can sell his products with the Indian Organic Logo which lauds the authenticity of the product in India and abroad. He/she can also sell the products at a premium price compared to products from conventional farming practices.
Step 7: Renewal
Every farmer enjoying the benefits of organic certification must be aware of the fact that the certification is not a one-time process. The certification underlines the fact that the farmer or the business will be under close surveillance by the certification agency.
The certified farms will be subjected to annual reviews and inspections to ensure compliance with the certification standard and he/she does not resort to any malpractices. The certified farmer must continue to adhere to the standards to retain the certification.
Time for Obtaining Organic Certification
The period for obtaining organic certificationvaries with the type of unit registered for the application. It can take a period ranging from 1 day to 3 years. The period of some of the units registered for organic certification is
| Unit | Time |
| Farm | 2 years |
| Fruit Orchard | 3 years |
| Diary Unit | 3 months |
| Food Processing Unit | 1 day |
This time can vary greatly depending on the certifying agency, the farmer or business, and several other factors.
Read More:
Conclusion
The process of organic certification is tiresome. It is expensive and time-consuming. Organic farming, contrary to conventional farming practices, does not produce substantially high yields. There is an exponentially growing demand for organic produce. This will fetch high profits for people who undertake organic farming practices against all odds.
This is where organic certification becomes handy. It serves as an object of assurance for consumers who are ready to spend high on healthy chemical-free produce. The Indian organic certification logo is a symbol of trust that carries its honor throughout the country and beyond. So the farmers should strive to attain the certification by strictly complying with the organic certification standards.
Latest Post
- June Issue (2025) – Times of Agriculture Magazine
- How to Create Modern Commercial Greenhouse Agriculture
- REACH NEW HEIGHTS WITH YOUR BUSINESS AT VIETSTOCK EXPO & FORUM 2025
- Revamping Waste: A wish list This World Environment Day
- Types of Banana in India : Health & wallet friendly fruit
- May Issue (2025): Times of Agriculture
- How to Grow Oyster Mushrooms at Home in India
- Top 10 Profitable Fruit Farming in India
- 5 Unique Hobby Farm Animals You Should Consider Domesticating










